Data Transmission: What Is It? Everything You Need to Know
Table of Contents

The sheer volume of analog and digital data moving across global business networks continues to scale at an unprecedented rate.
In this guide, we explore what data transmission is and how CDNs enable faster transfer across global digital systems.
What is Data Transmission?
Data transmission is the transfer of data from one digital device to another through wired or wireless network channels. It powers the digital world by routing information across network channels. From traditional copper-based hardware to contemporary wireless connectivity systems, these data streams now travel across a global wireless network to ensure precise communication between interconnected devices.
As we know, data transmission methods can involve different types of data, including both analog and digital formats, but in this blog, we focus on digital modulation, which encodes and decodes digital signals through two main methods: parallel transmission and serial transmission.
The effectiveness of data transmission relies heavily on the amplitude and transmission speed of the carrier channel, which directly determines the data transfer rate. The amount of data transferred within a given amount of time depends on how efficiently each data packet moves through the network.
Network congestion, latency, server health, and insufficient infrastructure can slow down the process of transmitting data and reduce overall performance. High-speed data transfer rates are essential when sending data for complex tasks such as online streaming and large file transfers.
Exploring the Different Types of Data Transmission
Data transmission serves as an essential infrastructure for global business communications. The process involves transferring digital information between network devices through multiple communication channels.
Directional Modes: Simplex vs. Half-Duplex vs. Full-Duplex
- Simplex: Data flows in one direction only, making it ideal for broadcasting applications.
- Half-duplex: Data flows in both directions, but only one direction at a time, suitable for error detection and controlled communication.
- Full-duplex: Data flows simultaneously in both directions, perfect for real-time interactions.
Synchronization Methods: Synchronous vs. Asynchronous
- Synchronous: Utilizes clock signals for precise timing, beneficial for high-speed data transfers.
- Asynchronous: Employs start/stop bits, adaptable for varying hardware capabilities.
Bit Transfer Techniques: Serial vs. Parallel
- Serial: Sends data bits sequentially, optimal for long-distance transfers.
- Parallel: Transmits multiple bits simultaneously, ideal for short-distance, high-volume data movement.
The Role of CDNs in Optimizing Data Transmission
Reliable data transmission is essential for modern digital services, but global networks face inherent challenges such as latency, congestion, and traffic spikes. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) address these challenges by distributing data closer to end users, enhancing speed, scalability, and reliability.
Minimizing Latency and Enhancing Transfer Efficiency
Data transmission performance is largely determined by how fast data packets move across carrier networks, especially when supporting high-bandwidth applications like 4K streaming, cloud services, and big data workloads. By caching and delivering content from edge locations closer to users, a CDN reduces the physical distance data must travel, which directly lowers latency and improves overall transfer efficiency across global networks.
Scaling Transfer Rates for Global Traffic Surges
Modern digital platforms generate massive volumes of data from mobile devices, IoT systems, and social media, creating traffic patterns that fluctuate rapidly and produce unpredictable load spikes. A CDN distributes these data requests across multiple geographically dispersed nodes, allowing data transmission rates to scale dynamically without overwhelming a single origin server or degrading user experience.
Strengthening Reliability and Data Security
Reliable data transmission requires more than speed; it depends on resilient routing and protection of sensitive information as data moves between systems. CDN architectures enhance reliability by eliminating single points of failure through distributed delivery, while built-in encryption and traffic management help safeguard sensitive data and support secure, real-time data processing across the network.
How CDNetworks Enables Efficient and Resilient Data Transmission
Optimized Global Delivery Infrastructure
With more than 2,800 Points of Presence (PoPs) in over 87 countries and regions, CDNetworks supports efficient data transmission at scale.
The global edge architecture of CDNetworks allows content and applications to be delivered from locations that are geographically and topologically close to end users, thereby reducing latency and lowering the distance data must travel for each request. By serving content from multiple edge sites instead of a single central origin server, CDNetworks minimizes network hops and enhances responsiveness for both static and dynamic traffic, especially for users spread across diverse geographic regions.
By serving content from multiple edge sites instead of a single central origin server, CDNetworks minimizes network hops and enhances responsiveness for both static and dynamic traffic, especially for users spread across diverse geographic regions.
CDNetworks’ global load balancing intelligently avoids overloading compute nodes by routing client requests or traffic to other potentially idle nodes. By optimizing network routes in this way, CDNetworks prevents localized bottlenecks and improves throughput consistency. Whether caching static content or accelerating dynamic application responses, this layer of optimization enhances delivery efficiency and reliability even under significant traffic load.
Intelligent Routing and Protocol Enhancements
CDNetworks enhances data transmission through smart routing and transport optimization. With E-Optimize, data flows are carried through a dynamically optimized transmission tunnel across CDNetworks’ global network, where routing, congestion control, and retransmission behavior are continuously adjusted to maintain high throughput and low latency over long-distance and unstable networks.
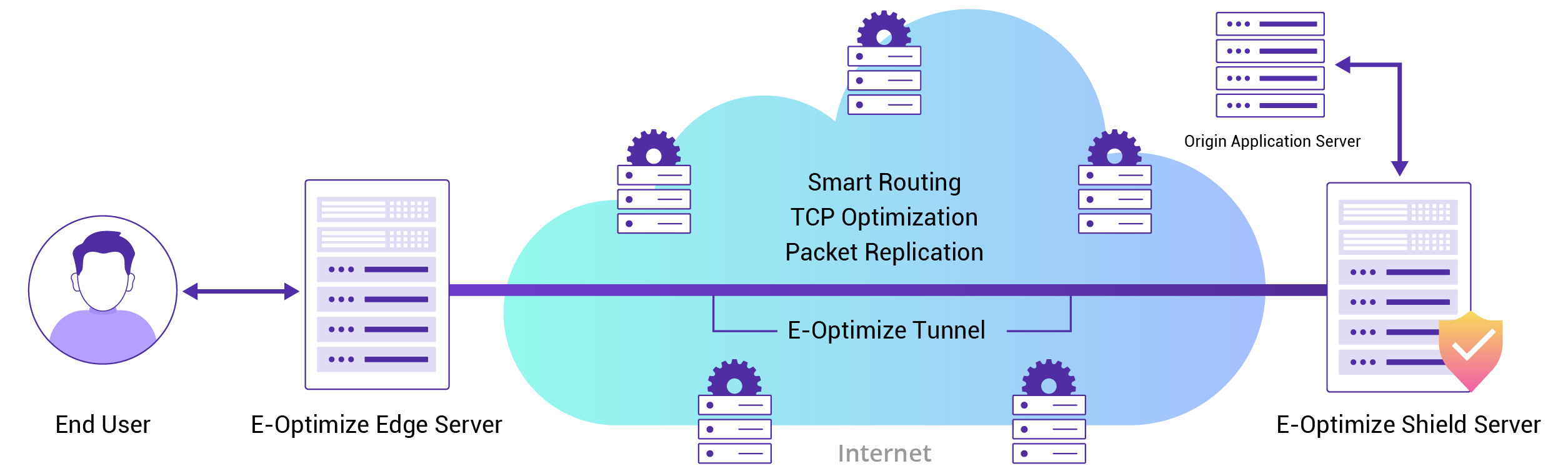
CDNetworks also supports modern transport protocols such as HTTP/2, QUIC, and TLS 1.3, which streamline connection overhead and enable faster, more secure sessions between clients and servers. These protocol enhancements, combined with connection multiplexing and optimized middle-mile connectivity, help deliver both static and dynamic content rapidly. Consequently, users experience faster data transfer at speeds that are orders of magnitude beyond traditional FTP and HTTP methods, whether transferring massive media files or multiple smaller assets.
Secure Delivery and Operational Intelligence
CDNetworks integrates security features directly into its data delivery fabric, including Web Application Firewalls (WAF), distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) mitigation, and bot detection. By filtering malicious traffic close to the source and away from origin infrastructure, CDNetworks preserves downstream bandwidth and reduces the likelihood of service interruption. Secure traffic handling ensures that sensitive data in motion remains protected while performance remains stable.
Data Transmission FAQ
1. What is Data Transmission and Why is It Important for Modern Businesses?
Data transmission is the process of sending and receiving digital information between devices, servers, and applications over computer networks. It underpins everything from web browsing and cloud services to video streaming and enterprise software.
For modern businesses, reliable data transmission is essential because enterprise operations rely on the rapid movement of massive datasets across geographically dispersed networks. Delays, packet loss, or unstable network connections can directly impact application performance, customer experience, and real-time decision-making.
2. How Do CDNs Improve Data Transmission Performance?
CDNs improve data transmission by distributing content and application traffic across a global network of edge servers. Instead of routing all requests through a single origin server, data packets are delivered from the closest available PoP.
This architecture reduces latency, lowers packet loss, and optimizes network resource utilization. CDNs also provide load balancing and congestion management, allowing large volumes of data to be transmitted efficiently even during traffic spikes or across long-distance network connections.
3. Why are CDNs Critical for Handling Large Amounts of Data and Global Traffic?
Centralized network architectures often struggle when delivering large amounts of data across multiple regions. Long distances, limited bandwidth, and network congestion can increase the time required for data packets to travel between servers and end users.
CDNs solve these challenges by caching and accelerating content at the edge, closer to end users. By spreading traffic across multiple network devices and PoPs, CDNs maintain consistent performance, support wireless connectivity, and ensure that data transmission remains stable regardless of user location or traffic volume.
4. How CDNetworks Outperforms Traditional FTP and HTTP for Data Transmission?
By leveraging a global network of over 2,800 PoPs and high-capacity backbone links, CDNetworks accelerates data transfers by up to 100x compared to traditional FTP and HTTP methods. Its 200 Tbps total bandwidth capacity ensures seamless support for high-volume media, enterprise-grade applications, and real-time services.
To maximize efficiency and reliability, CDNetworks employs multi-path transfer and global load balancing, allowing data to follow the most optimal routes. These mechanisms not only reduce packet loss but also strengthen performance for both small files and massive data flows.
More To Explore
Key Cybersecurity Statistics and Emerging Trends for 2026
A data-driven overview of cybersecurity statistics and emerging threats shaping 2026, including AI-driven attacks, DDoS, API exploitation, ransomware, phishing.
CDNetworks Successfully Mitigated a 1.01 Tbps Ransom DDoS Attack on a Major Software Download Platform
This attack was part of an organized RDDoS campaign that persisted for over a month. CDNetworks Flood Shield 2.0 ensured legitimate users experienced zero disruption.